What is a PV combiner box?
A PV combiner box combines the power of multiple solar panels into a single line, then transmitted to the inverter. This configuration minimizes the number of cables required and saves on equipment costs.
The main components of a PV solar combiner box typically include PV string fuses, molded case DC circuit breakers, DC surge protectors, bus bars, and terminals. Additionally, some models may be equipped with monitoring devices.
The specifications and dimensions of a solar combiner box may vary depending on the installation environment and usage conditions.
Before diving into the specifics of a solar combiner box, a basic understanding of photovoltaic systems is required. A photovoltaic system, also known as a solar power system, is designed to convert solar energy into usable electrical energy using photovoltaic technology.
PV combiner boxes play a very key role in solar PV systems, especially in larger systems. They act as a central node that groups the wiring of the individual modules. This arrangement not only organizes the electrical connections but also improves safety.
In addition to managing the wiring, combiner boxes have built-in overcurrent protection that mitigates voltage spikes that can damage the inverter, extending its life.
Some junction boxes have monitoring systems that can alert users of potential problems. These devices require minimal maintenance, usually only occasional checks for leaks and loose connections.

Why do you need a PV combiner box?
There are several reasons why a PV combiner box is essential, especially when it comes to wiring a solar panel system. Although it is not necessary for installations with fewer than four channels, its benefits come into play in larger installations. The main features of a solar combiner box include:
Line integration: It bundles multiple lines from a solar panel into a single output, simplifying connection to the inverter and reducing hardware costs.
Equipment protection: The junction box improves the safety of connected equipment, such as inverters, by providing overcurrent protection. This helps prevent damage from surges.
Quick disconnect: In the event of power fluctuations, the junction box can be quickly disconnected, minimizing potential risks.
Unified management: It allows centralized management of all front solar groups, making it easier to monitor and maintain the system.
If your solar system requires these features, it is necessary to understand and purchase a PV junction box.
When should I use a PV combiner box?
If you have more than three solar panel strings, you must use a PV combiner box in your solar power system. Its main functions include improving inverter protection and providing a quick shutdown mechanism in case of sudden voltage fluctuations.
A PV combiner box simplifies inverter wiring, making the entire system easier to manage while helping to reduce material and installation costs. This is especially beneficial in large, multi-string systems.
Here are some of the top reasons to consider using a solar collection box:
Protection: Protects the inverter from overcurrent and overvoltage conditions that can cause equipment failure.
Simplified wiring: Consolidating multiple panel outputs into a single connector can reduce wiring complexity, making installation and maintenance easier.
Cost-effective: Using a junction box can reduce hardware costs by minimizing wiring and reducing installation time.
Quick shutdown capability: In the event of a power surge, the junction box can be quickly disconnected from the system, increasing safety.
Components of a PV combiner box
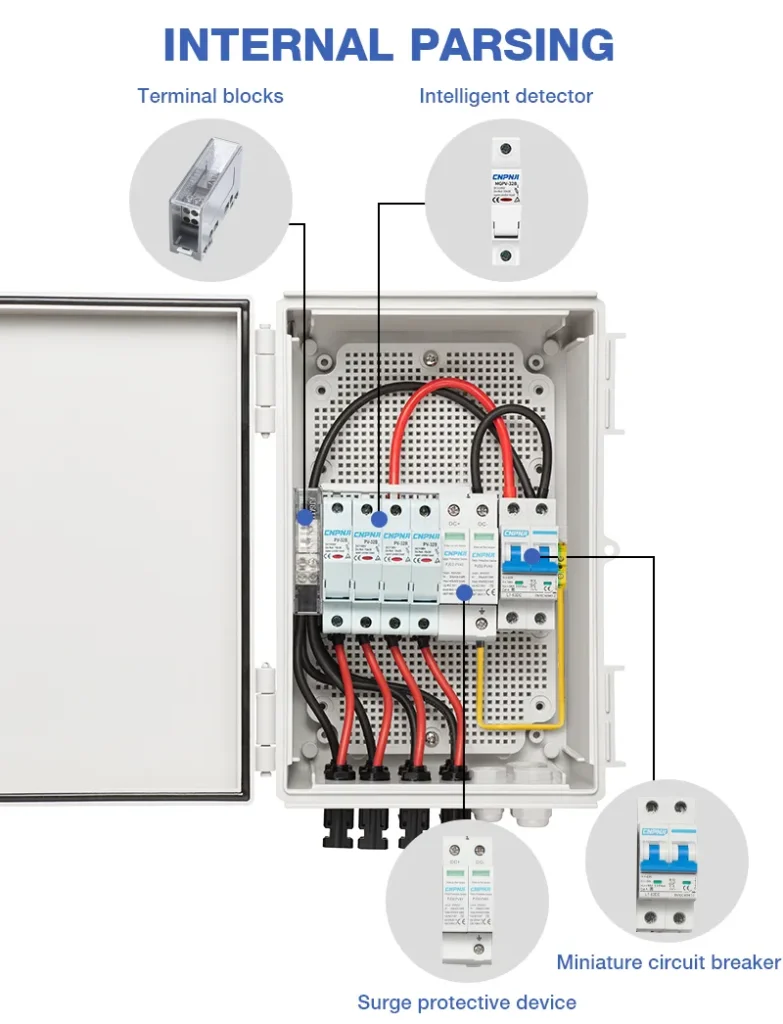
A typical PV combiner box is equipped with several basic components that work together to ensure that the solar power system operates efficiently and safely. Key components include:
Molded case circuit breaker (MCCB): MCCBs protect the circuits of a solar power system, especially for high-power PV systems. They typically handle currents from 63A to 630A and provide strong overload protection.
PV fuse: Fuses are important to prevent overcurrent conditions by interrupting the flow of current in the event of a fault. They help block reverse currents and protect cables and other equipment from damage. They are mostly located on the input side and consist of a fuse holder and fuse core and interrupt the affected circuit in emergency situations such as overcurrent or short circuit. If the fuse blows, it should be replaced depending on the situation.
DC Surge Protection Device (SPD): SPDs protect the system from temporary voltage spikes by shunting the surges to ground. They are designed to protect sensitive electrical equipment from potential damage caused by surges. Damage caused by surges can result in shortened life or equipment failure.
DC Disconnect Switch or DC Circuit Breaker: These switches are located at the output of the junction box and can be used to manually disconnect or isolate the circuit in the event of a surge or short circuit, increasing safety during maintenance.
Bus Bar: This conductive metal strip acts as a multiple connection point to connect multiple incoming wires to one unit. It is often used to connect the negative or ground wire of a solar panel and is used to collect, distribute, and transfer energy within a PV system.
Terminal Blocks: Terminal blocks function similarly to bus bars and are usually made of ABS composite materials instead of metal to connect the various circuits within the junction box.
Enclosure: The enclosure is the physical housing for all the components in the combiner box. It is made of materials such as polycarbonate (PC) or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and is designed to meet IP65 standards for protection against dust and water while also being UV resistant to withstand the harsh conditions and difficult environmental conditions.
In addition, many PV combiner boxes can be equipped with monitoring devices that can manage and observe system performance in real time. These devices vary in their specifications and sizes to meet different installation requirements.
How to Choose a PV Combiner Box
There are several important factors to consider when choosing the right PV combiner box for your solar project:
Number of input channels: Determine the number of solar panels you want to connect in the combiner box. Choose a combiner box that can accommodate all of the solar components in your system.
Cable size compatibility: Make sure the combiner box can support the appropriate cable diameter. Commercial applications generally use larger wiring configurations than residential configurations.
Overcurrent protection: Choose a combiner box with an appropriate voltage rating and overcurrent protection that fits the size of the solar panel. The overcurrent protection should be able to handle reasonable voltage spikes based on the system specifications.
Intended use and configuration: Determine where the combiner box will be installed and what configuration you want. Decide if you want a simple template or a template with more features. Also consider whether the combiner box will be wall-mounted or placed on the floor, as this will impact size and style.
Enclosure classification: Different environments require different enclosure classifications to protect internal components from moisture and other potential damage. For installations in humid areas, choose a combiner box with a higher rating to avoid moisture ingress, which can cause premature wear on internal wiring.
Quality and durability: Look for an enclosure made of sturdy materials that can withstand harsh conditions. Make sure they have features like tight-fitting lids to keep moisture and debris out and sturdy, durable enclosures for long-term use.
Safety features: Choose a combiner box with built-in safety features like surge protectors, circuit breakers, and grounding terminals to greatly reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
Module and inverter compatibility: Before completing your purchase, check that the combiner box is compatible with your specific solar panels and inverter. Incompatibility can cause performance issues or damage.
Quality of internal components: Make sure all internal components meet local standards and regulations. Note that these may vary from country to country.
Customized requirements: Since manufacturers may not have a ready-made solution for every situation, be prepared to customize the combiner box if your requirements are complex. Customization will ensure that it meets the exact specifications of your system.
Contact Mingguan Electric to confirm your PV plan.

How a PV combiner box works
PV combiner boxes work in a series of systematic steps that improve the efficiency and safety of your solar system:
Collection: Each individual solar panel absorbs solar energy to produce direct current (DC), which is sent to the combiner box through separate input channels.
Confluence: The combiner box combines the outputs of all connected panels into a single DC output. This simplified output makes it easy to connect to the inverter.
Protection: Combiner boxes are equipped with protective devices such as fuses or circuit breakers. These components protect the system from overcurrent conditions, preventing damage to panels and other equipment.
Monitoring: More advanced PV combiner boxes may have built-in monitoring systems that track power measurements and help diagnose problems that arise to ensure optimal solar system operation.
Considerations for Mounting a Solar Combiner Box
When installing a solar combiner box, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity:
Accessibility: Choose a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and inspection. This facilitates routine inspections and necessary repairs.
Orientation: Mingguan Electric recommends installing the PV combiner box in a north-facing location. This orientation allows for more shade throughout the day, reducing the risk of overheating from direct sunlight.
Waterproofing: It is important to install the combiner box in a location that is relatively unaffected by adverse weather conditions. Although many enclosures are weatherproof, additional protection can help extend their lifespan.
Proximity to solar panels: Place the generator combiner box close to existing solar panels. This will minimize the length of wiring required and greatly reduce the risk of electrical faults between the panels and the combiner box.
Environmental conditions: Consider the specific environmental conditions in which the combiner box will be installed. For example, if you are installing in a humid area, an enclosure with a higher power rating should be used to prevent moisture ingress, which can cause internal damage.
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation at the installation site. Good air circulation will help dissipate heat generated inside the enclosure, providing additional protection to the internal components.
The above six factors should be carefully considered during the installation process to improve the efficiency and durability of the solar PV combiner box and ensure that the solar system is reliable and safe.
How to Maintain a Solar Combiner Box
Maintaining a solar combiner box can go a long way in extending its lifespan and maintaining optimal performance, especially since they are often installed outdoors and exposed to various environmental factors. Here are the key maintenance steps to follow:
Safety First: Always unplug the solar combiner box from the power source before performing any maintenance. This is essential for your safety. Perform maintenance carefully and responsibly.
Clean the Interior: Clean the interior of the combiner box regularly to prevent the buildup of dust and dirt. Use a soft, damp towel and soap to clean. Then dry the interior thoroughly with a dry towel.
Inspect Internal Wire Connections: Inspect all wire connections inside the combiner box. Wear insulated gloves when inspecting exposed areas for signs of loosening or oxidative deterioration. If materials need to be replaced, make sure this task is performed by a qualified person with electrical knowledge.
Replace a blown fuse: If a fuse is blown, it must be replaced because it cannot be reused. Before replacing a fuse, unplug the circuit breaker and check the voltage with a multimeter.
Check the surge protector: Check the surge protector’s status window; it must be green. A red light means it is defective and needs to be replaced.
Final inspection: After all maintenance is complete, do a thorough inspection to make sure everything has been properly cared for and protected.
