What is a distribution box?
A distribution box is a critical component in any electrical system, acting as a central hub for distributing electricity to various circuits. Think of it as the heart of your electrical setup, ensuring power flows where it needs to go while keeping everything safe and organized. The primary role of a distribution box is twofold: power distribution and protection.
In terms of power distribution, the box ensures that electricity is evenly distributed across different circuits in your home, office, or industrial space. But it’s not just about sending power out—it also plays a crucial role in protecting your electrical system. By housing essential safety components like circuit breakers and fuses, the distribution box helps prevent overloads, short circuits, and other electrical hazards. In short, it’s your first line of defense against electrical mishaps.
The Role in the Electrical System
In an electrical system, the distribution box acts as a control center. It connects to the main power supply and divides that power into smaller circuits that feed into different areas or devices. Whether you’re lighting up a room or powering heavy machinery, it all starts with the distribution box. Without it, you’d be left with a chaotic mess of wires and a much higher risk of accidents.
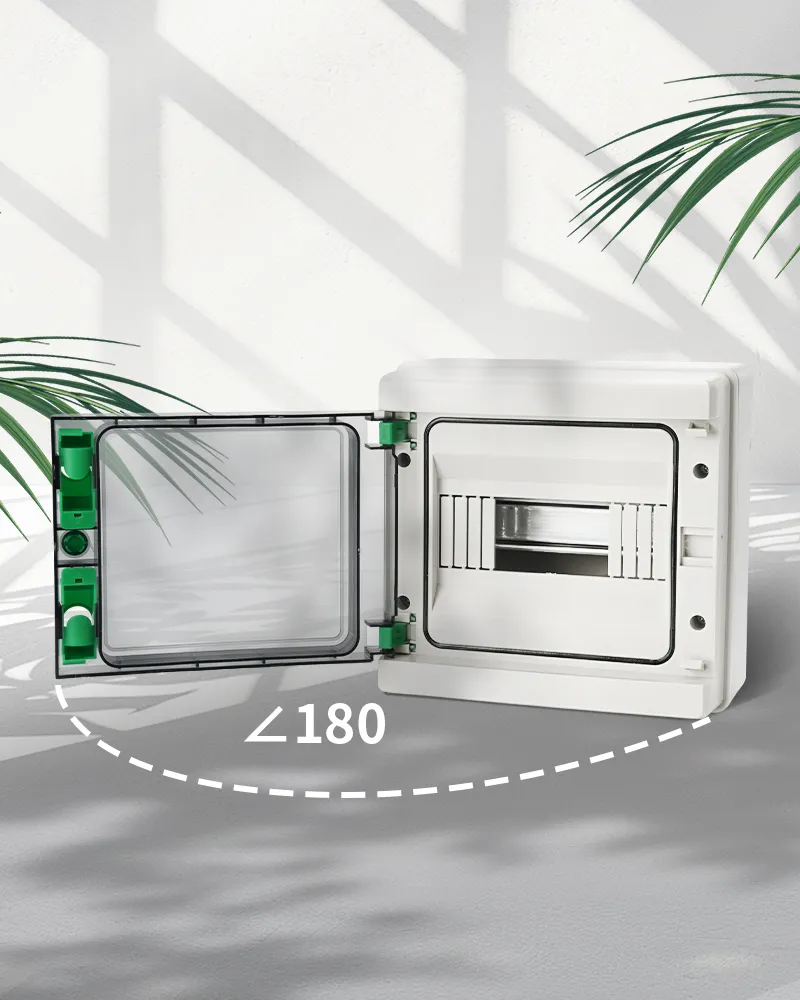

Types of Distribution Boxes
Classification by Structure
Distribution boxes come in various shapes and sizes depending on their intended use. Let’s break down some common types based on structure:
- Fixed Panel Distribution Box: This type is often used for low-power applications where simplicity is key. The components are mounted on a fixed panel, making installation straightforward but limiting flexibility. It’s great for basic setups where you don’t need to frequently change or expand your system.
- Drawer-Type Distribution Box: If you’re looking for something more modular, the drawer-type distribution box is your friend. With its pull-out drawers, this design makes maintenance and expansion easy. Need to add new components or fix an issue? Just slide out the drawer! This makes it ideal for environments where flexibility and frequent maintenance are necessary.
- Power and Lighting Control Distribution Box: Built for industrial use—specifically for vertical installations where space can be tight—this type handles both power distribution and lighting control in tough environments like factories or warehouses.
Classification by Material
The material used in a distribution box can tell you a lot about its intended environment:
- Metal Distribution Box: Known for durability and strength, metal boxes are perfect for industrial settings where they might take a beating from heavy machinery or harsh conditions. They’re built to last and can withstand more wear and tear than their plastic counterparts.
- Plastic Distribution Box: On the flip side, plastic boxes are lightweight and more commonly found in residential or light commercial settings. They’re easier to install and handle but might not be as durable as metal boxes in harsher environments.
Special Types
Sometimes you need something more specialized:
- Explosion-Proof Distribution Box: If you’re working in hazardous environments—think areas with explosive gases or dust—you’ll need an explosion-proof distribution box. These are designed to prevent sparks or heat from igniting dangerous substances around them, making them essential in industries like mining or chemical manufacturing.
Components of Distribution Box
Shell
The shell is what keeps everything inside the distribution box safe from external factors like dust, water, or physical damage. Depending on the environment where it’s installed, the shell can be made from materials like steel (for added strength) or plastic (for lighter-duty applications).
One important factor to consider when choosing a shell is its protection level—often indicated by an IP (Ingress Protection) rating like IP66. This rating tells you how well the box protects against things like dust and water ingress. For example, an IP66-rated box is completely dust-tight and protected against powerful water jets—perfect for outdoor or industrial use where exposure to harsh elements is common.
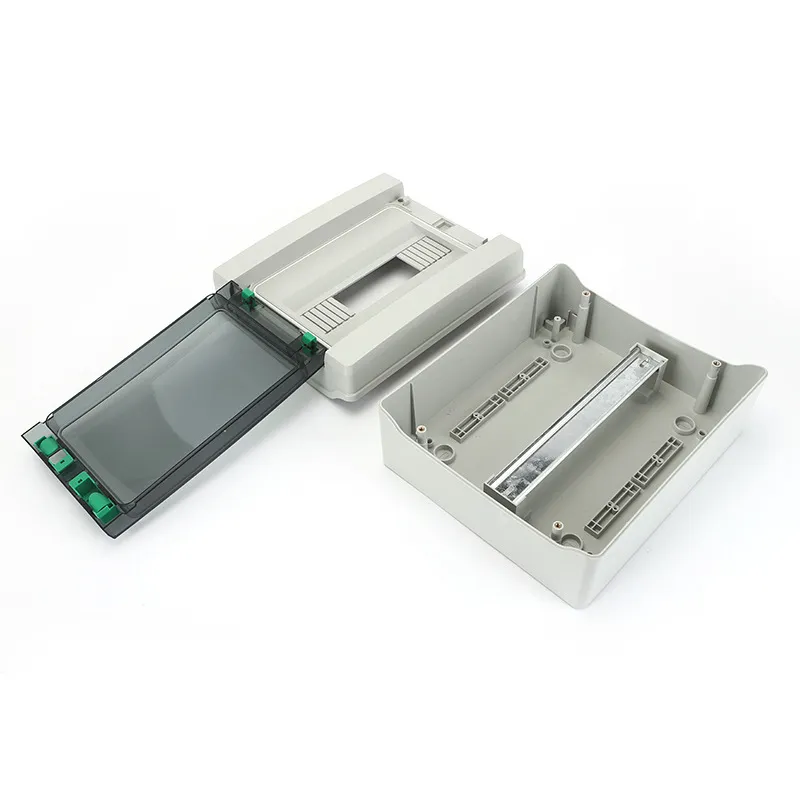

Internal Components
Ever wondered what’s going on inside a distribution box? It’s not just a jumble of wires; it’s a carefully organized system designed to distribute and manage electricity efficiently and safely. Inside, you’ll typically find components like circuit breakers, contactors, fuses, distribution bars, and sometimes more advanced monitoring equipment. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring that electricity flows smoothly while protecting the system from faults like overloads or short circuits.
Inside every distribution box lies an array of components that keep your electrical system running smoothly:
- Circuit Breaker: This little hero prevents overloads and short circuits by cutting off power when things go wrong—like when too much current flows through a circuit.
- Contactor and Fuse: These two work together to control the flow of electricity within the system. The contactor acts as a switch that controls high-power circuits, while fuses provide extra protection by breaking the circuit if something goes wrong.
- Leakage Protector: Safety first! A leakage protector ensures that any stray currents (which could cause electric shocks) are quickly cut off before they become dangerous.

Distribution Bar
The distribution bar—usually made from copper or aluminum—ensures efficient power distribution within the box itself. Copper is particularly popular because it’s highly conductive, meaning less energy is lost during transmission compared to other materials like aluminum.
Additional Equipment
Many modern distribution boxes come equipped with additional monitoring tools to help keep everything running smoothly.
- Thermometer: Measures temperature inside the box to prevent overheating.
- Hygrometer: Monitors humidity levels—important if you’re working in damp environments.
- Indicator Lights: These provide visual signals about the status of different circuits within the box so you can quickly spot any issues without needing specialized tools.
Main Functions of Distribution Boxes
Power Distribution Function
At its core, the main job of a distribution box is to distribute power from the main supply to various branch circuits. Imagine your home or office as a tree—the distribution box is like the trunk that splits into branches (circuits), each feeding power to different parts of the building. Whether you’re running a hairdryer in your bathroom or operating machinery in a factory, it’s the distribution box that ensures each device gets just the right amount of electricity.
Electrical Protection Function
Safety is another critical function of the distribution box. It protects your electrical system from faults like overloads and short circuits using circuit breakers and fuses.
- Circuit breakers act as automatic switches—they cut off power when they detect an issue.
- Fuses, on the other hand, break apart when too much current flows through them, stopping electricity from causing damage.
Without these protective measures in place, electrical faults could lead to overheating, fires, or even electrocution. So next time your circuit breaker trips during a thunderstorm or when you plug in too many devices at once, remember—it’s doing its job!
Monitoring and Control Function
Modern distribution boxes don’t just distribute power; they also help you keep an eye on things with real-time monitoring features.
- Some boxes come equipped with tools like thermometers (to monitor temperature) and hygrometers (to check humidity levels). These devices ensure that your electrical system operates within safe limits and can alert you to potential problems before they become serious.
In industrial settings where power usage is high and conditions can be harsh, this kind of monitoring is especially important for preventing accidents and downtime.

Distribution Box Size
Introduction to Standard Sizes
Distribution boxes come in various sizes depending on their intended use:
- For residential applications, smaller boxes are typically used—often with space for around 4–12 circuits. These compact designs are perfect for homes where power needs are relatively low.
- Industrial distribution boxes are much larger and can accommodate dozens of circuits, along with additional monitoring equipment and safety features. You might see sizes ranging from 24-circuit panels to even larger custom setups designed for factories or large commercial buildings.
How to Choose the Right Size?
Choosing the right size distribution box depends on two main factors: your load requirements and your available installation space.
- For basic home installations (lighting, appliances), a smaller box will suffice.
- Industrial facilities running heavy machinery around the clock will need something much larger—both in terms of physical size and capacity.
It’s also important to think about future expansion. If you plan on adding more circuits later (e.g., for new equipment), it’s worth investing in a slightly larger box upfront to save yourself time and money later on.
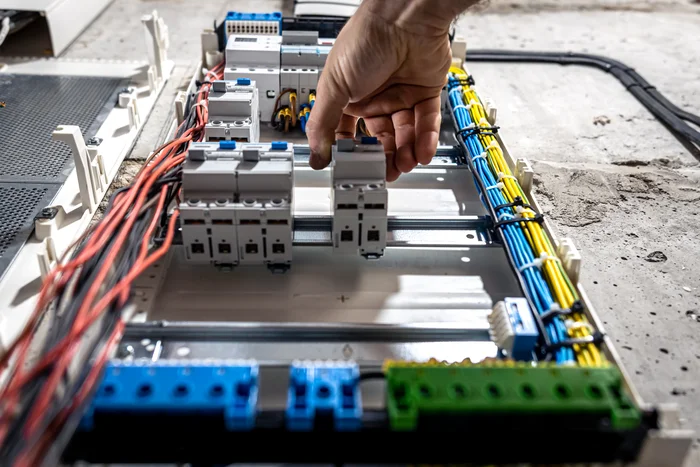
Distribution Box Application
Home Application
In homes, distribution boxes play an essential role in managing electricity safely and efficiently. They ensure that each room gets enough power without overloading any single circuit—so you can run your washing machine while watching TV without worrying about tripping a breaker! Plus, they include safety features like leakage protectors that help prevent electrical shocks.
Whether you live in a small apartment or a large house, having a well-designed distribution box ensures that all your gadgets and appliances get the juice they need without putting your home at risk.
Commercial and Industrial Applications
When it comes to commercial buildings or industrial facilities, things get more complicated—and more powerful! These spaces often have much higher energy demands than homes due to heavy machinery or large-scale lighting systems.
In these environments:
- Distribution boxes need to handle bigger loads while offering advanced safety features like explosion-proof designs for hazardous areas (think chemical plants).
- Modular layouts allow for easy maintenance without shutting down entire sections of the facility.

How do I install the distribution box?
Detailed Installation Steps
Installing a distribution box isn’t rocket science—but it does require careful planning and attention to detail. Here’s how to do it right:
- Choose a Suitable Location: Select a well-ventilated, easily accessible spot for maintenance. The location should be free from moisture or corrosive elements to prevent long-term damage. Ideally, install the box near the main power supply for convenience.
- Install the Base: Securely mount the base of the distribution box on a flat surface. Use a level to ensure it’s perfectly horizontal. The base should be attached firmly using expansion bolts or steel nails, depending on the surface.
- Connect Each Circuit: Follow the wiring diagram carefully when connecting each circuit. Ensure all wires are connected to their designated terminals, paying attention to polarity and grounding requirements.
- Test the System: Before securing everything in place, run tests to ensure proper functionality. Check that all circuits are working correctly and that safety devices like circuit breakers and fuses respond as expected.
- Secure the Box: Once everything checks out, securely fasten the distribution box cover and label each circuit for easy identification during future maintenance.
Installation Precautions
While installing a distribution box, keep these important precautions in mind:
- Avoid Humid or Corrosive Environments: Moisture can cause serious damage over time, leading to short circuits or corrosion of internal components. If you must install in such environments, consider using an IP-rated (Ingress Protection) box that offers protection against dust and moisture.
- Comply with Local Safety Standards: Always ensure your installation complies with local electrical codes and safety regulations to avoid potential hazards and legal issues down the road.
- Use Proper Tools: Ensure you have insulated tools and protective gear when working with electrical systems to prevent accidents.
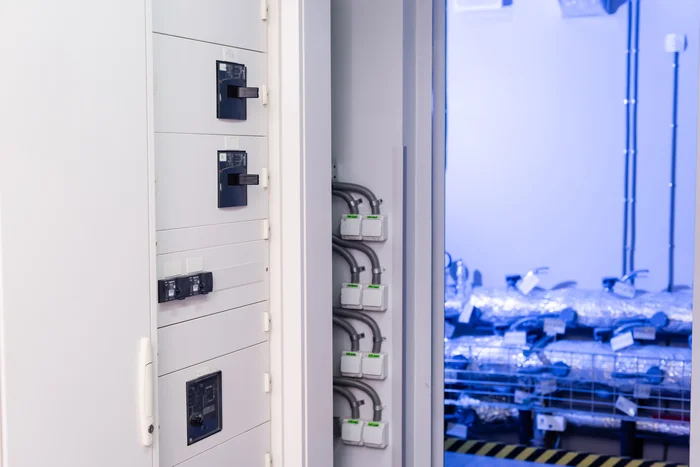

What are the requirements for the material of the distribution box shell?
Fire Resistance and Durability
The material of a distribution box shell is critical for safety and durability.
- Fire Resistance: The shell must be made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and resist fire. Steel is commonly used in industrial settings due to its strength and fire resistance, while high-grade plastic is often preferred in residential installations for its lightweight properties.
- Durability: In industrial environments where heavy machinery operates, steel shells are ideal because they can endure rough conditions without compromising safety. In contrast, plastic shells are suitable for homes where physical impact is less likely.
In case of an electrical fault or fire, these materials help contain internal issues safely, preventing them from escalating into larger hazards.
Protection Level (IP Level)
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating is crucial when selecting a distribution box shell, especially for outdoor or harsh environments.
- An IP66-rated box offers complete protection against dust and powerful water jets, making it ideal for outdoor installations or areas exposed to moisture and dust.
- This level of protection ensures that internal components remain safe from environmental hazards that could otherwise lead to malfunctions or safety risks.
What are the functions of the distribution box?
Power Distribution
The primary function of a distribution box is to efficiently distribute electrical power throughout a building or facility.
- It acts as a central hub that takes power from the main supply and divides it into smaller branch circuits.
- This organized distribution ensures that all parts of the system receive adequate power without overloading any single circuit.
Electrical Protection
A key role of the distribution box is protecting your electrical system from faults such as overloads, short circuits, or power surges.
- Circuit breakers automatically disconnect power when they detect an issue.
- Fuses break apart when too much current flows through them, stopping electricity from causing damage.
Without these protective measures, electrical faults could lead to overheating, fires, or even electrocution.
Monitoring and Control
Modern distribution boxes often come equipped with monitoring tools that allow real-time performance tracking.
- Devices like thermometers (to monitor temperature) and hygrometers (to check humidity levels) ensure that your electrical system operates within safe limits.
In industrial settings where power usage is high, this monitoring helps prevent accidents by detecting potential problems early on.
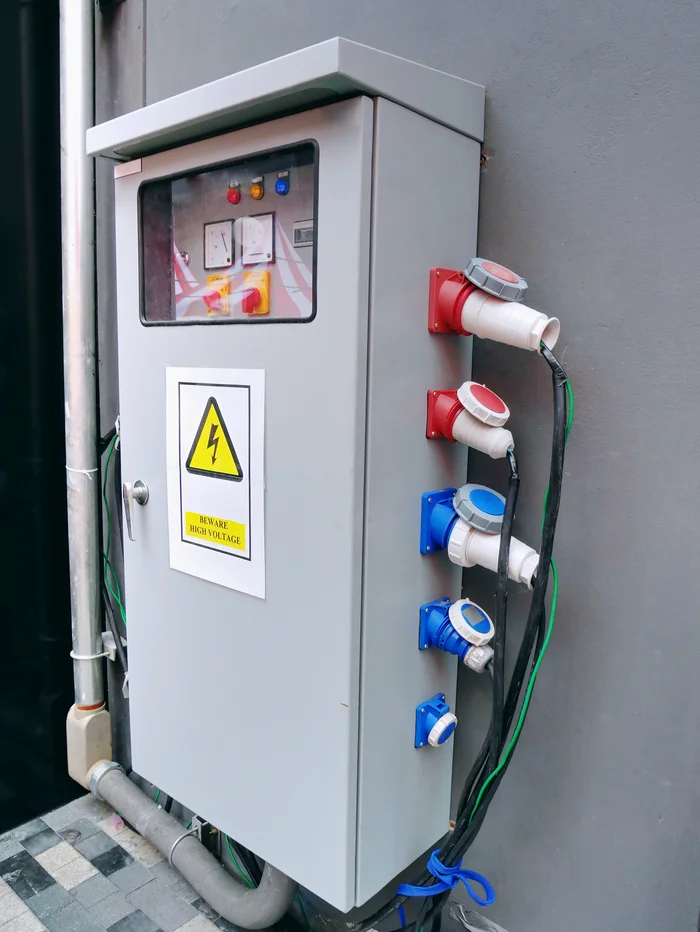

What is the purpose of the distribution box?
Home Use
In homes, distribution boxes provide safe power management by distributing electricity from a single source to various circuits throughout the house.
- They ensure each room gets enough power without overloading any single circuit—whether you’re running kitchen appliances or charging your phone in the living room.
- Additionally, they offer protection against electrical faults through circuit breakers and leakage protectors.
Commercial and Industrial Use
In commercial and industrial settings, distribution boxes handle much larger loads of electricity.
- They distribute power to heavy machinery, lighting systems, and other equipment while ensuring that electrical faults don’t lead to costly downtime or dangerous situations.
- Features like modular designs for easy maintenance and explosion-proof shells for hazardous areas are often necessary in these environments.
What Is the Difference Between a Junction Box and a Distribution Box?
A junction box primarily serves as an enclosure where electrical wires are spliced together or where conduits meet.
- It’s used for connecting different sections of wiring but doesn’t manage large-scale power distribution or offer much in terms of protection.
On the other hand, a distribution box goes beyond just connecting wires—it actively manages power distribution across multiple circuits while housing protective devices like circuit breakers.
| Feature | Junction Box | Distribution Box |
| Primary Function | Connects wires | Distributes power across circuits |
| Protection | Limited | Includes circuit breakers/fuses |
| Application | Smaller-scale wiring connections | Broader power management |
While both boxes play essential roles in an electrical system, their functions differ significantly: junction boxes focus on connections, while distribution boxes handle broader power management tasks.
What is the difference between a distribution board and a distribution box?
A distribution board is typically larger and more complex than a distribution box. It is commonly used in commercial or industrial settings where managing higher electrical loads is necessary. Distribution boards serve as centralized control points, distributing electricity across large areas or multiple circuits. They contain multiple circuit breakers or fuses, allowing for organized power distribution and protection. The primary function of a distribution board is to manage and protect various circuits from overloads and short circuits.
In contrast, a distribution box is smaller, simpler, and often used in residential settings or small commercial spaces where fewer circuits need to be managed. While both devices serve the purpose of distributing electricity, they differ in size, complexity, and typical use cases. Distribution boxes are more compact and can be portable, making them suitable for environments with lower power demands or temporary setups like outdoor events or construction sites.
| Feature | Distribution Board | Distribution Box |
| Size | Larger, more complex | Smaller, simpler |
| Typical Use | Commercial/industrial | Residential/small commercial |
| Functionality | Centralized control of multiple circuits | Protects electrical connections |
| Installation | Fixed installation | Can be portable |
Are fuse boxes and distribution boxes the same?
No, fuse boxes and distribution boxes are not exactly the same. A fuse box uses fuses to protect circuits from overloads by physically breaking when too much current flows through them. Once a fuse blows, it must be replaced.
In contrast, modern distribution boxes use circuit breakers instead of fuses. Circuit breakers are more reliable because they can be reset after tripping due to an overload or short circuit, making them safer and more convenient for managing today’s electrical systems. The shift from fuse boxes to distribution boxes reflects advancements in safety and ease of maintenance.
Do I need an electrician to install the distribution box?
Importance of Expertise
Yes, you absolutely need an electrician to install a distribution box. Although it might seem like a straightforward task, improper installation can lead to serious hazards such as electrical fires or shocks. Electricians bring specialized knowledge and experience that ensures the installation is done safely and in compliance with local regulations.
Electricians undergo extensive training to handle complex electrical systems, ensuring that connections are made correctly and that grounding is properly implemented. A single mistake—such as incorrect wiring or poor grounding—can result in catastrophic consequences. Moreover, professional installation ensures that your system meets safety standards, which is crucial for both personal safety and the longevity of your electrical system.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Non-professionals often make mistakes that can lead to serious problems.
- Incorrect wiring: Miswiring can cause short circuits or fires.
- Overcrowding: Fitting too many wires into a small space can lead to overheating.
- Improper Grounding: Without proper grounding, excess electrical current has nowhere to go, increasing the risk of shocks.
These are just a few reasons why it’s best to leave this job to professionals.
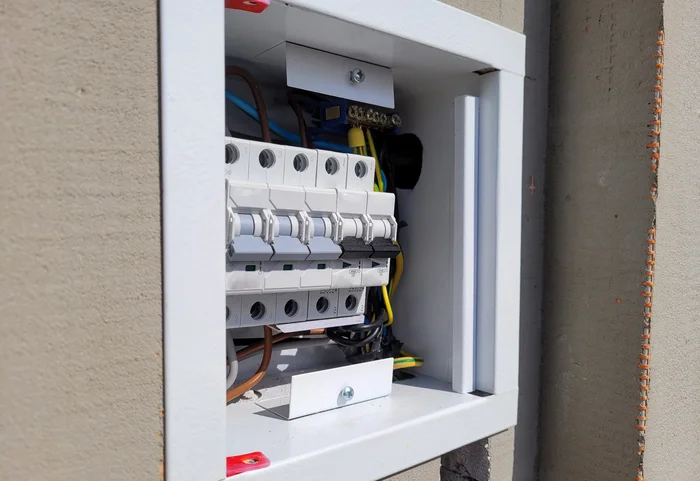

Can I put the distribution box on the wall?
Yes, you can mount a distribution box on the wall, but there are important considerations:
- Ventilation: Ensure the location has proper airflow to prevent overheating.
- Height Requirements: Install the box at a height that allows easy access for maintenance but keeps it out of reach of small children for safety reasons.
- Compliance with Local Codes: Always check local regulations regarding placement height and other safety requirements before proceeding with installation.
How do I choose a distribution box?
Choose According to Load Requirements
The first step in choosing a distribution box is determining your current load requirements:
- For small homes with basic appliances, a smaller box will suffice.
- For industrial facilities running heavy machinery, you’ll need a larger box with higher capacity.
It’s also wise to consider future expansion. If you anticipate adding more circuits later (e.g., for new appliances or additional rooms), choose a distribution box with extra space so you don’t have to replace it later.
Environmental Considerations
Where will your distribution box be installed? If it’s going outdoors or in harsh environments (like factories), opt for one made from durable materials like steel with a high IP rating (e.g., IP66) for protection against dust and water ingress. For indoor use in homes or offices, lighter materials like plastic may suffice.
Safety Function Considerations
Safety should always be top priority when selecting a distribution box.
- Ensure it includes essential protection features like leakage protection and overload protection.
- Verify that the distribution box complies with local safety regulations—this ensures both your safety and legal compliance.
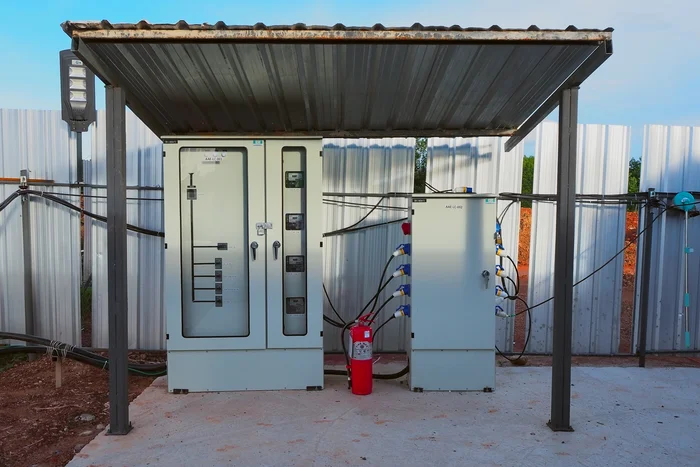

What do I need to consider when buying a distribution box?
Scalability
One key factor when buying a distribution box is scalability.
- Will you be able to add more circuits without replacing the entire unit?
- Look for boxes with extra slots or modular designs that allow for easy expansion as your power needs grow.
Ease of Installation
Another important consideration is how easy the distribution box will be to install and maintain.
- Are internal components clearly labeled? This simplifies both installation and troubleshooting.
- Does it come with features like pre-drilled holes for mounting or built-in cable management systems? These features can save time during installation.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Finally, perform a cost-benefit analysis before making your purchase:
- While it might be tempting to go for the cheapest option, remember that quality matters when it comes to electrical systems.
- A slightly more expensive but reliable distribution box will likely save you money in the long run by reducing maintenance costs and preventing potential hazards.
